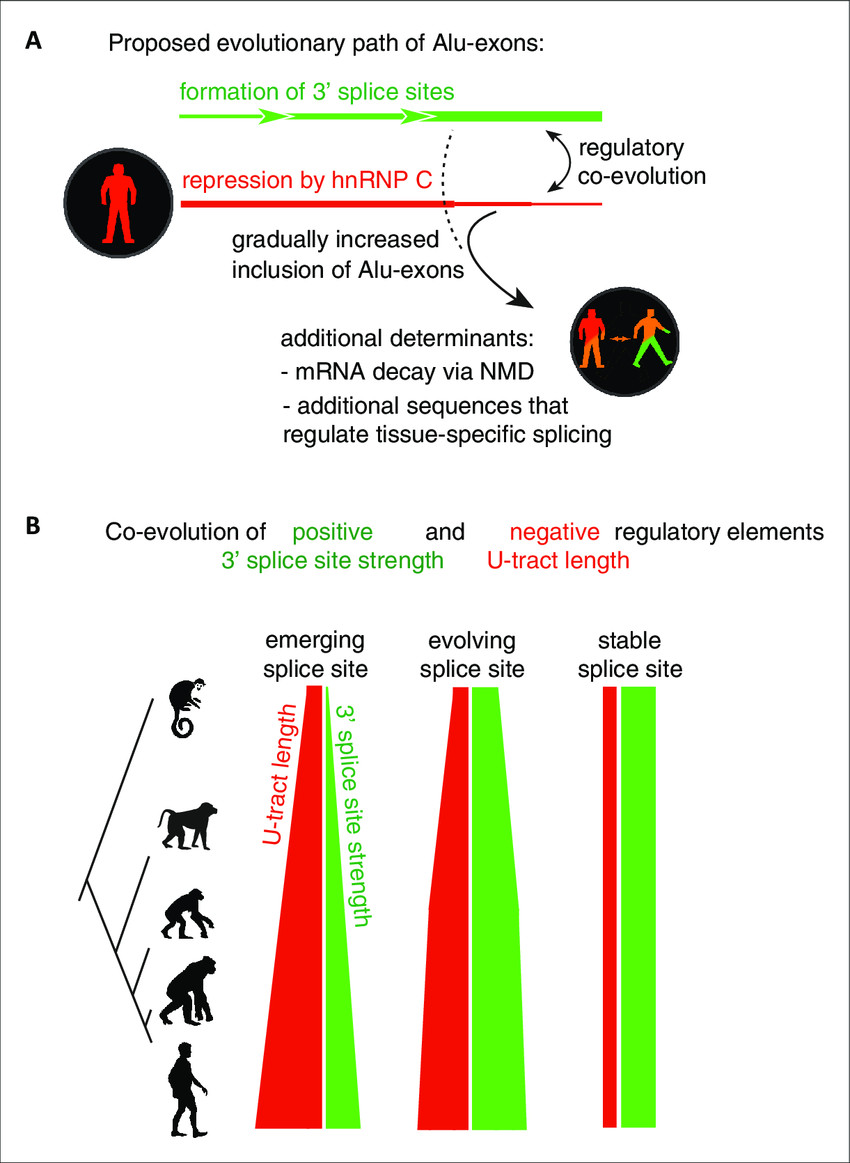
Repressive elements co-evolve with splice site sequences at cryptic
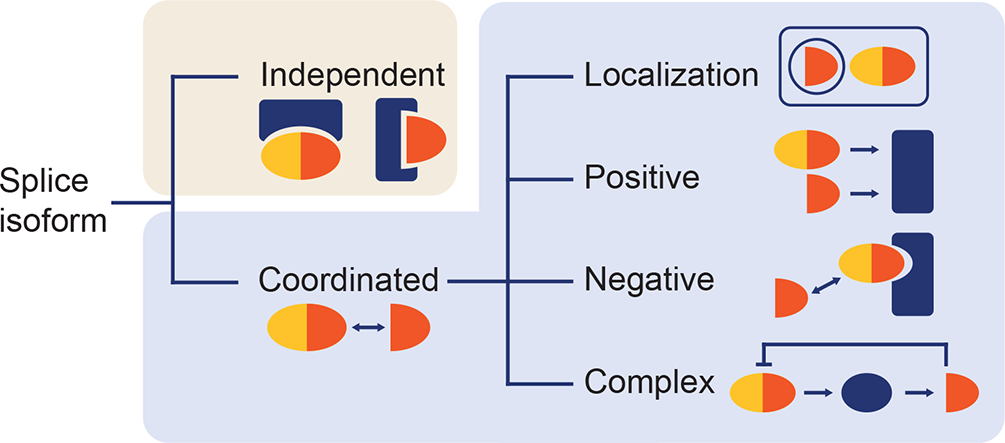
How alternative splicing changes the properties of plant proteins
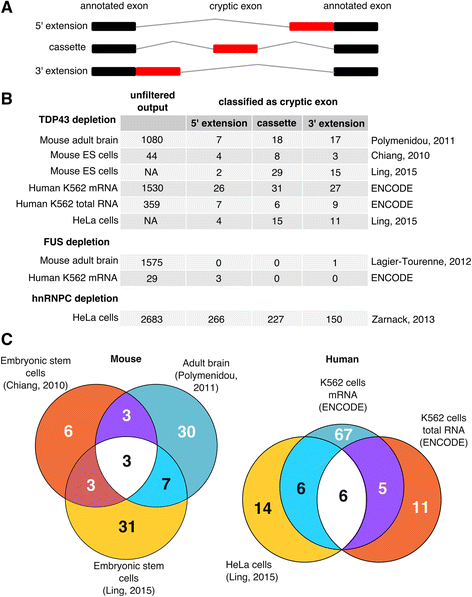
Quantitative analysis of cryptic splicing associated with TDP-43

The TER1 intron contains all elements required for spliceosomal

RNA splicing factors as oncoproteins and tumour suppressors
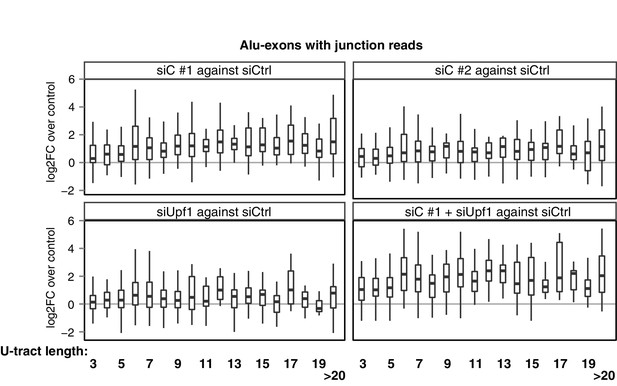
Splicing repression allows the gradual emergence of new Alu-exons

Quantitative analysis of cryptic splicing associated with TDP-43 depletion, BMC Medical Genomics
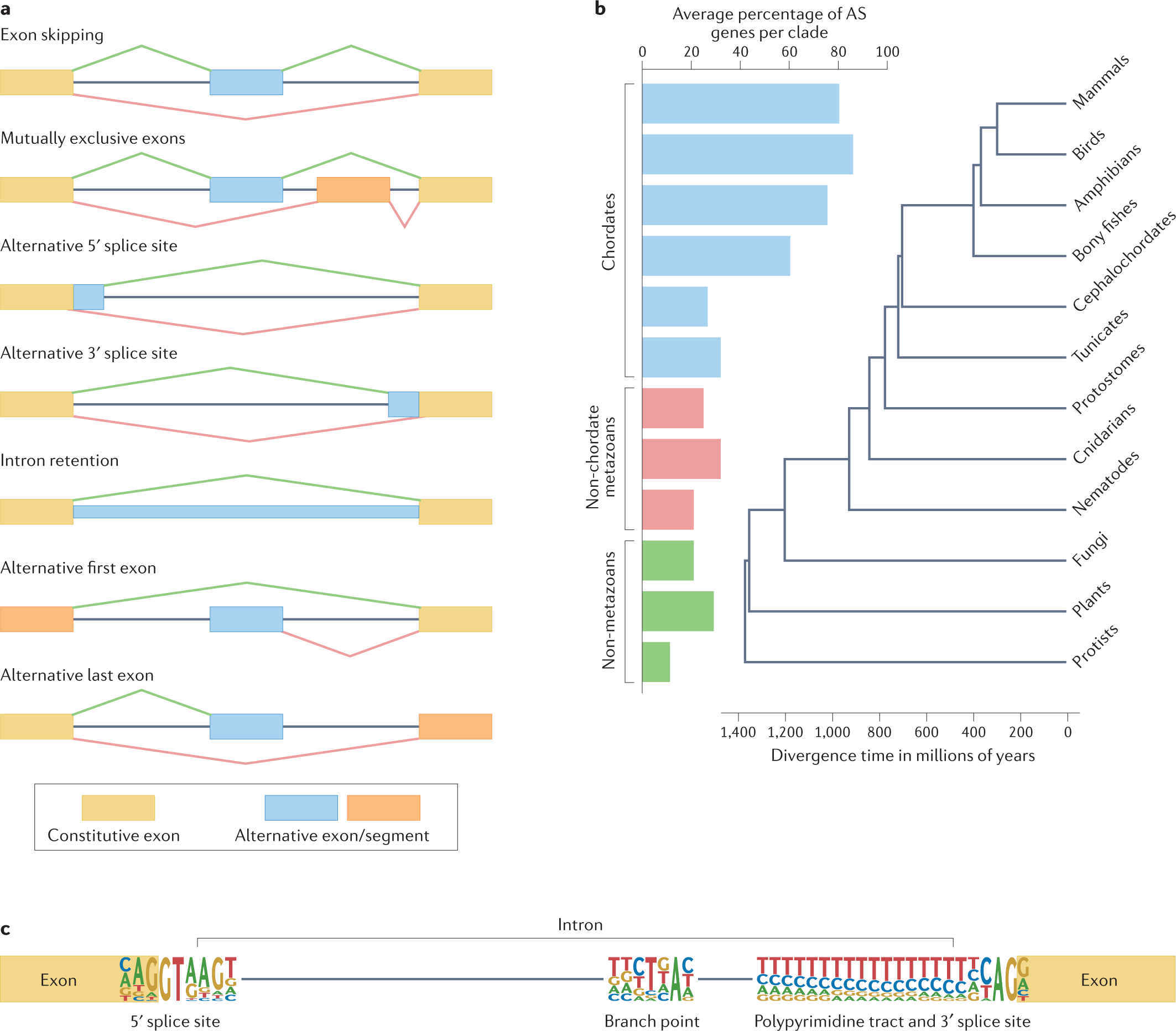
Alternative splicing as a source of phenotypic diversity

Lessons from non-canonical splicing

Regulation of pre-mRNA splicing: roles in physiology and disease
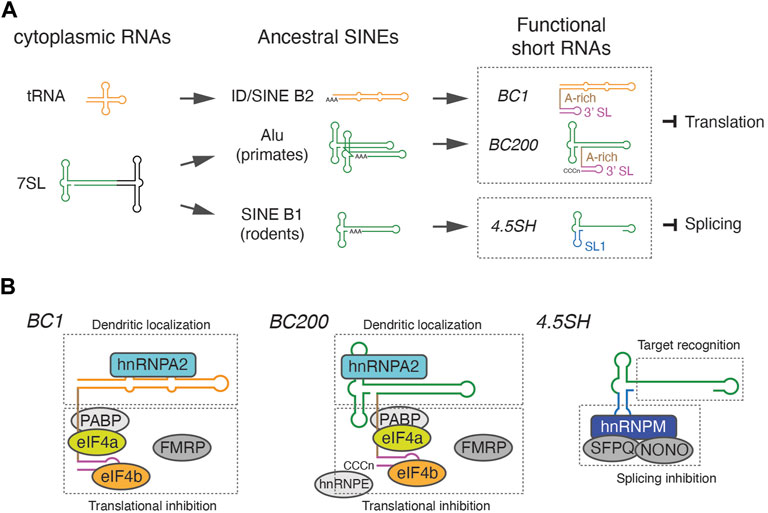
Frontiers SINE-derived short noncoding RNAs: their evolutionary origins, molecular mechanisms, and physiological significance

The role of alternative pre-mRNA splicing in cancer progression

Alu-exons are associated with reduced gene expression. (A) Expression
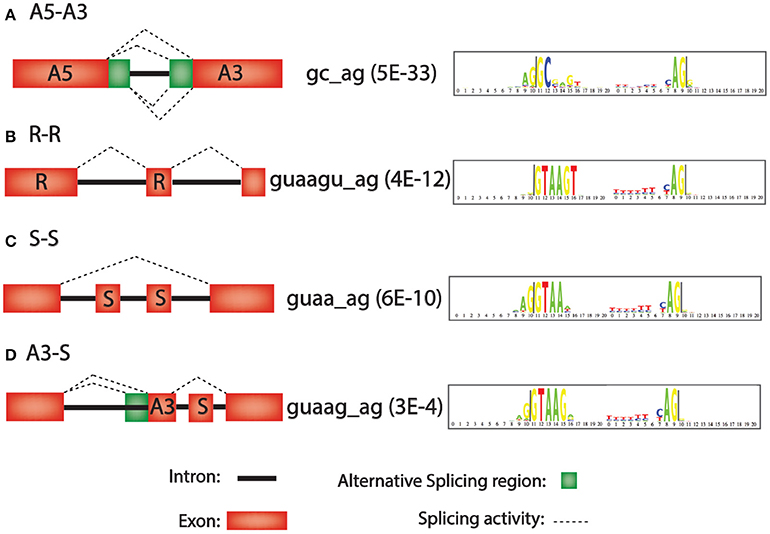
Frontiers A Bioinformatics-Based Alternative mRNA Splicing Code
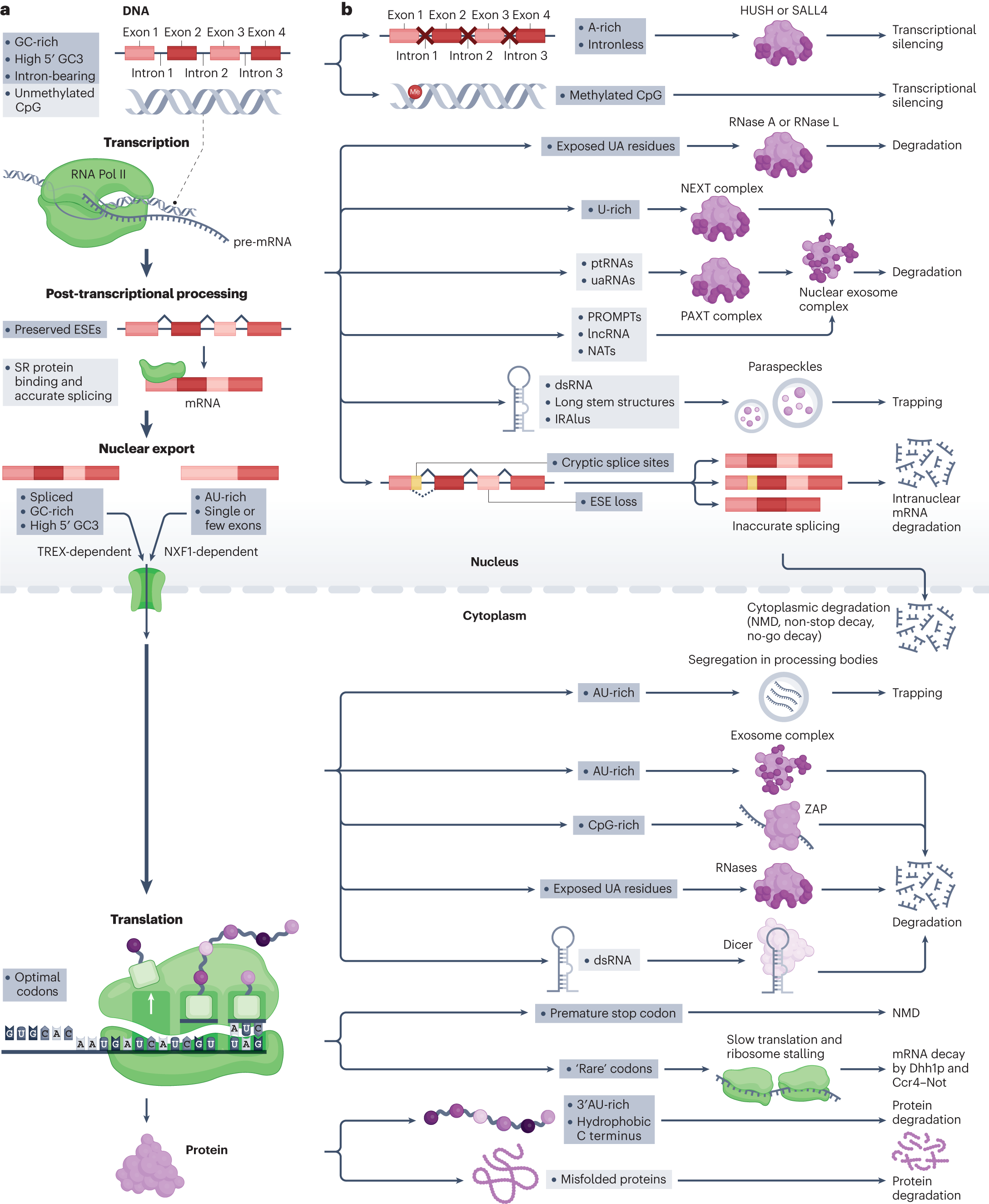
Selection on synonymous sites: the unwanted transcript hypothesis








